Cobalt 2 Chloride Hexahydrate Formula
khabri
Sep 09, 2025 · 7 min read
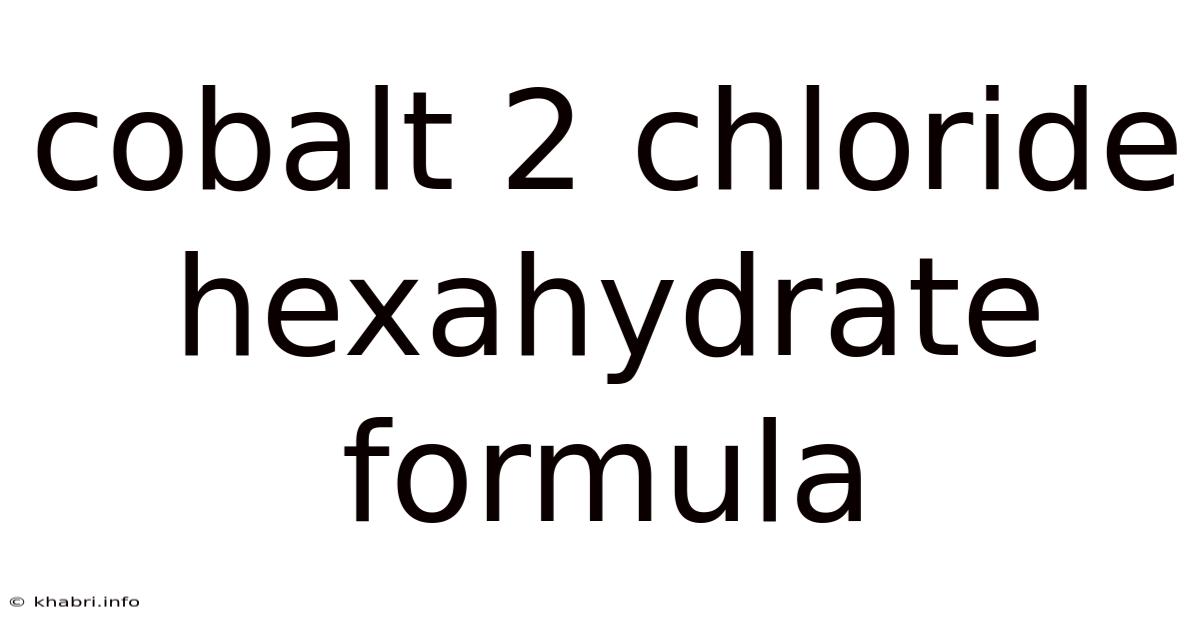
Table of Contents
Decoding Cobalt(II) Chloride Hexahydrate: A Deep Dive into its Formula, Properties, and Applications
Cobalt(II) chloride hexahydrate, often represented by the formula CoCl₂·6H₂O, is a fascinating compound with a vibrant pink color and a wide array of applications. Understanding its formula unlocks a deeper appreciation for its unique properties and its significance in various fields, from chemistry education to industrial processes. This article will comprehensively explore the formula, delve into its chemical and physical properties, examine its diverse applications, and address frequently asked questions.
Understanding the Formula: CoCl₂·6H₂O
The formula CoCl₂·6H₂O itself tells us a great deal about this compound. Let's break it down:
-
Co: Represents the cobalt(II) ion, indicating that cobalt is present in its +2 oxidation state. Cobalt is a transition metal, known for its variable oxidation states and the colorful complexes it forms.
-
Cl₂: Represents two chloride ions (Cl⁻), each carrying a single negative charge, balancing the +2 charge of the cobalt ion.
-
·6H₂O: This part signifies the presence of six water molecules associated with each formula unit of cobalt(II) chloride. These water molecules are not simply trapped within the crystal lattice; they are coordinated directly to the cobalt ion, forming a complex called a hydrate. This coordination significantly influences the compound's properties. The water molecules are integral to the structure and are responsible for many of its characteristic features.
Chemical and Physical Properties of Cobalt(II) Chloride Hexahydrate
Cobalt(II) chloride hexahydrate exhibits a unique set of properties that make it a valuable reagent in various applications:
-
Appearance: Its most striking characteristic is its vibrant pink color. This color arises from the d-d electronic transitions within the cobalt(II) ion's electronic configuration, influenced by the surrounding ligands (chloride ions and water molecules).
-
Solubility: It is highly soluble in water, a property directly related to the polar nature of both the cobalt(II) ion and the water molecules. This high solubility makes it easily handled and utilized in aqueous solutions.
-
Hygroscopic Nature: This compound is highly hygroscopic, meaning it readily absorbs moisture from the atmosphere. This absorption can lead to a change in its color and appearance, often transitioning to a blue color as the water molecules are lost. This property is exploited in certain humidity indicators.
-
Melting Point: It has a relatively low melting point compared to anhydrous cobalt(II) chloride, primarily due to the presence of the water molecules that weaken the crystal lattice interactions.
-
Crystal Structure: Cobalt(II) chloride hexahydrate adopts a specific crystal structure, typically a monoclinic crystal system. The arrangement of the cobalt ions, chloride ions, and water molecules within this structure dictates many of its physical and chemical behaviors.
-
Color Change with Dehydration: As mentioned earlier, the dehydration of cobalt(II) chloride hexahydrate results in a dramatic color change. The loss of water molecules alters the coordination environment around the cobalt(II) ion, leading to a shift in its electronic absorption spectrum, causing the characteristic pink color to change to a deep blue. This reversible color change is the basis of many of its applications.
Synthesis and Preparation of Cobalt(II) Chloride Hexahydrate
The synthesis of cobalt(II) chloride hexahydrate is relatively straightforward. It's often prepared through the reaction of cobalt(II) oxide or cobalt(II) carbonate with hydrochloric acid. The reaction typically proceeds as follows:
CoO(s) + 2HCl(aq) + 6H₂O(l) → CoCl₂·6H₂O(aq)
or
CoCO₃(s) + 2HCl(aq) + 5H₂O(l) → CoCl₂·6H₂O(aq) + CO₂(g)
The resulting aqueous solution is then evaporated carefully to allow for the crystallization of cobalt(II) chloride hexahydrate. The crystals are usually pink and can be further purified through recrystallization techniques. Care must be taken during this process to avoid contamination and to ensure the formation of high-quality crystals.
Diverse Applications of Cobalt(II) Chloride Hexahydrate
The unique properties of cobalt(II) chloride hexahydrate make it a versatile compound with a wide range of applications:
-
Humidity Indicators: Its hygroscopic nature and color change upon dehydration make it ideal for use in humidity indicators. These indicators change color as the humidity levels fluctuate, providing a visual representation of the moisture content in the air. This application is used in various settings, from weather forecasting to industrial processes.
-
Chemical Synthesis: It serves as a precursor in the synthesis of other cobalt compounds and complexes. Its role is crucial in many organic and inorganic chemical reactions where cobalt is needed as a catalyst or a reagent.
-
Electroplating: It finds application in electroplating processes to deposit a thin layer of cobalt onto metal surfaces. This application improves the surface properties of the metal, enhancing its corrosion resistance, hardness, and overall appearance.
-
Pigments: It's used as a component in the formulation of certain pigments, especially those used in paints, inks, and coatings. The vibrant pink color contributes to the overall aesthetic appeal of these products.
-
Dyes and Inks: Its ability to produce a range of colors depending on its hydration state is exploited in certain dyes and inks for various applications.
-
Catalysis: Cobalt(II) chloride hexahydrate acts as a catalyst in various chemical reactions. Its catalytic properties stem from the ability of the cobalt ion to participate in redox reactions, facilitating the conversion of reactants into desired products.
-
Medicine: Though not as commonly used as other cobalt compounds, it may find some niche applications in medicine, for example, in specific types of diagnostic or therapeutic agents.
Safety Precautions and Handling
Like many chemical compounds, cobalt(II) chloride hexahydrate requires careful handling:
-
Avoid Inhalation: Inhalation of the dust can be harmful to the respiratory system. Always handle it in a well-ventilated area or wear appropriate respiratory protection.
-
Eye and Skin Contact: Avoid direct contact with skin and eyes. Wear appropriate protective equipment, including gloves and eye protection. If contact occurs, flush the affected area with plenty of water.
-
Disposal: Dispose of waste according to local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What is the difference between anhydrous cobalt(II) chloride and cobalt(II) chloride hexahydrate?
A1: The key difference lies in the presence of water molecules. Anhydrous cobalt(II) chloride (CoCl₂) is devoid of water molecules, while cobalt(II) chloride hexahydrate (CoCl₂·6H₂O) has six water molecules coordinated to each cobalt(II) ion. This difference significantly impacts their physical properties, particularly their color and solubility. Anhydrous CoCl₂ is typically blue, while the hexahydrate is pink.
Q2: Can cobalt(II) chloride hexahydrate be dehydrated?
A2: Yes, it can be dehydrated by heating it gently. The heating process removes the water molecules, resulting in the formation of anhydrous cobalt(II) chloride (CoCl₂), which exhibits a blue color. This dehydration is a reversible process; the anhydrous form can be rehydrated by exposing it to moisture.
Q3: What are the environmental concerns associated with cobalt(II) chloride hexahydrate?
A3: While not inherently highly toxic, cobalt compounds can pose environmental concerns if released in large quantities. Improper disposal can contaminate soil and water sources. It's crucial to handle and dispose of this compound responsibly according to local environmental regulations.
Q4: Is cobalt(II) chloride hexahydrate toxic?
A4: Cobalt(II) chloride hexahydrate is considered moderately toxic. While it's not highly toxic in small amounts, ingestion or prolonged exposure can lead to health problems. Always handle it with caution and follow appropriate safety measures.
Conclusion
Cobalt(II) chloride hexahydrate, represented by the formula CoCl₂·6H₂O, is a remarkable compound with a captivating pink color and a fascinating array of properties. Its unique characteristics, stemming from the interplay between the cobalt(II) ion and the coordinated water molecules, lead to a wide range of applications across various industries and scientific disciplines. From humidity indicators to chemical synthesis and electroplating, this compound plays a significant role in our modern world. Understanding its formula and properties empowers us to appreciate its importance and handle it responsibly. Remember to always prioritize safety when working with this compound.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Laboratory Procedures For Veterinary Technicians
Sep 09, 2025
-
Identify The Structure Labeled 1
Sep 09, 2025
-
1 1 Dibromo 2 Chlorocyclopropane
Sep 09, 2025
-
A Multiple Regression Model Has
Sep 09, 2025
-
The Personality Puzzle Chapter 5
Sep 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Cobalt 2 Chloride Hexahydrate Formula . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.