Combustion Of Methane Balanced Equation
khabri
Sep 13, 2025 · 6 min read
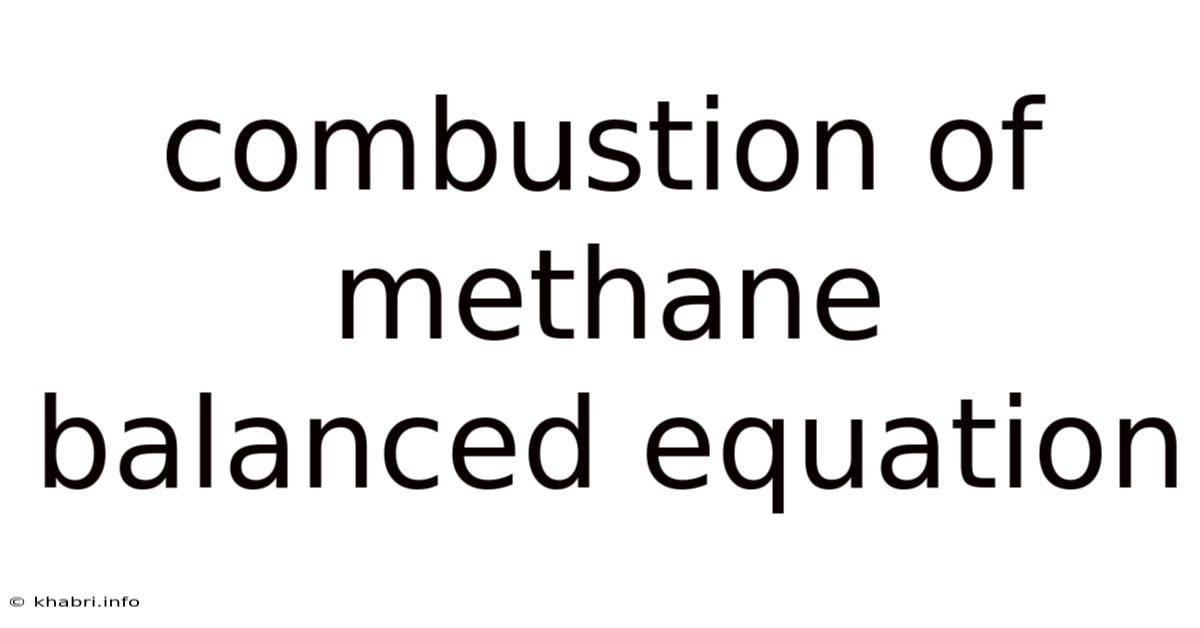
Table of Contents
Understanding the Combustion of Methane: A Deep Dive into the Balanced Equation and Beyond
The combustion of methane, a simple hydrocarbon, is a fundamental chemical process with vast implications across various industries and our daily lives. Understanding the balanced equation for this reaction is crucial for grasping its energy implications, environmental impact, and practical applications. This article will provide a comprehensive exploration of the methane combustion reaction, delving into the balanced equation, the underlying chemistry, its applications, and frequently asked questions. We'll also explore the broader context of combustion reactions and the importance of balanced chemical equations in understanding chemical processes.
The Balanced Equation for Methane Combustion
The simplest and most common form of methane combustion involves reacting methane (CH₄) with oxygen (O₂) to produce carbon dioxide (CO₂) and water (H₂O). The balanced chemical equation for this reaction is:
CH₄ + 2O₂ → CO₂ + 2H₂O
This equation indicates that one molecule of methane reacts with two molecules of oxygen to produce one molecule of carbon dioxide and two molecules of water. The equation is balanced because the number of atoms of each element is the same on both the reactant (left) and product (right) sides of the equation. This is crucial because it reflects the law of conservation of mass – matter cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction.
Understanding the Chemistry Behind the Reaction
The combustion of methane is an exothermic reaction, meaning it releases heat. This heat release is the primary reason methane is used as a fuel. The reaction occurs in several steps, involving the breaking and forming of chemical bonds. Let's break down the process:
-
Initiation: The combustion process begins with the initiation step, which requires an initial input of energy, often in the form of a spark or flame. This energy breaks the bonds within the methane and oxygen molecules, forming highly reactive free radicals.
-
Propagation: Once initiated, the reaction propagates through a chain reaction involving free radicals. These highly reactive species react with oxygen and methane molecules, breaking bonds and forming new ones. The propagation steps are responsible for the majority of the heat released during combustion. Examples of these propagation steps include:
- •CH₃ + O₂ → •CH₂O + •OH
- •CH₃ + O₂ → HCHO + •HO₂
- •OH + CH₄ → •CH₃ + H₂O
-
Termination: The chain reaction eventually terminates when free radicals combine to form stable molecules, ending the combustion process. Examples of termination steps include:
- •CH₃ + •CH₃ → C₂H₆
- •OH + •OH → H₂O₂
Complete Combustion vs. Incomplete Combustion
The balanced equation presented above represents complete combustion. This occurs when there is sufficient oxygen available for all the methane to react completely, forming only carbon dioxide and water. However, if the oxygen supply is limited, incomplete combustion occurs. This results in the formation of other products, such as carbon monoxide (CO) and soot (carbon particles). Incomplete combustion is less efficient and produces harmful byproducts. The equations for incomplete combustion are more complex and vary depending on the oxygen availability. For instance, one example of incomplete combustion could be:
2CH₄ + 3O₂ → 2CO + 4H₂O
This equation shows the formation of carbon monoxide instead of carbon dioxide, highlighting the danger of inadequate oxygen supply during methane combustion.
Applications of Methane Combustion
Methane combustion is a cornerstone of numerous industries and plays a vital role in our daily lives. Its primary application is as a fuel source:
- Heating: Natural gas, primarily composed of methane, is widely used for residential and industrial heating.
- Cooking: Many homes and restaurants use natural gas for cooking, relying on the heat produced by methane combustion.
- Electricity Generation: Power plants utilize methane combustion to generate electricity, converting chemical energy into electrical energy.
- Transportation: While less common than gasoline or diesel, compressed natural gas (CNG) vehicles utilize methane as a fuel source, offering a relatively cleaner-burning alternative.
- Industrial Processes: Various industrial processes, such as cement production and metal smelting, utilize methane combustion for their energy needs.
Environmental Impact of Methane Combustion
While methane combustion is a crucial energy source, its environmental impact cannot be ignored. Complete combustion produces carbon dioxide, a major greenhouse gas contributing to climate change. Incomplete combustion produces even more harmful pollutants, including carbon monoxide, a toxic gas. Therefore, efficient combustion technologies and strategies to reduce methane emissions are crucial to mitigate the environmental impact of this important process. The development and implementation of technologies to capture and utilize carbon dioxide from combustion processes are also actively being researched and implemented to minimize the contribution of methane combustion to global warming.
The Importance of Balanced Chemical Equations
Balanced chemical equations are not just a formality; they are fundamental tools in chemistry. They provide:
- Quantitative Information: Balanced equations allow for precise stoichiometric calculations, enabling chemists to determine the exact quantities of reactants needed and the amounts of products formed. This is vital in industrial processes, laboratory experiments, and environmental assessments.
- Understanding Reaction Stoichiometry: They reveal the molar ratios of reactants and products, enabling the prediction of yields and the identification of limiting reactants.
- Predicting Reaction Products: The balanced equation clearly identifies the products formed during a reaction, which is essential for understanding reaction pathways and potential hazards.
- Conservation of Mass: The balanced equation illustrates the law of conservation of mass, ensuring that the total mass of reactants equals the total mass of products.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What are the products of methane combustion?
A: In complete combustion, the products are carbon dioxide (CO₂) and water (H₂O). Incomplete combustion can also produce carbon monoxide (CO) and soot (carbon particles).
Q: Why is methane a good fuel?
A: Methane is an excellent fuel because its combustion is highly exothermic, releasing a significant amount of heat energy. It is also relatively abundant and readily available.
Q: What is the difference between complete and incomplete combustion?
A: Complete combustion occurs when sufficient oxygen is present, resulting in the formation of carbon dioxide and water. Incomplete combustion occurs when oxygen is limited, producing carbon monoxide and soot in addition to carbon dioxide and water.
Q: Is methane combustion environmentally friendly?
A: No, methane combustion is not environmentally friendly. While it's a crucial energy source, it produces carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas contributing to climate change. Incomplete combustion also releases harmful pollutants.
Conclusion
The combustion of methane, as represented by its balanced equation CH₄ + 2O₂ → CO₂ + 2H₂O, is a fundamental chemical reaction with profound implications. Understanding this reaction, including its chemistry, applications, and environmental impact, is vital for addressing global energy demands while minimizing environmental consequences. The balanced equation itself serves as a cornerstone for understanding the stoichiometry of the reaction and for conducting quantitative analyses. Continued research and development in cleaner combustion technologies and carbon capture methods are essential for harnessing the benefits of methane combustion while mitigating its environmental impact. By continuing to refine our understanding of this fundamental process, we can strive towards a more sustainable energy future.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Check Your Recall Unit 5
Sep 13, 2025
-
Economic Growth Is Depicted By
Sep 13, 2025
-
Lab Exercise 26 Somatic Senses
Sep 13, 2025
-
2 8b Angles Of Triangles
Sep 13, 2025
-
Draw Three Isomers Of C2h2cl2
Sep 13, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Combustion Of Methane Balanced Equation . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.