Ch3 Ch2 3ch Ch3 2
khabri
Sep 12, 2025 · 6 min read
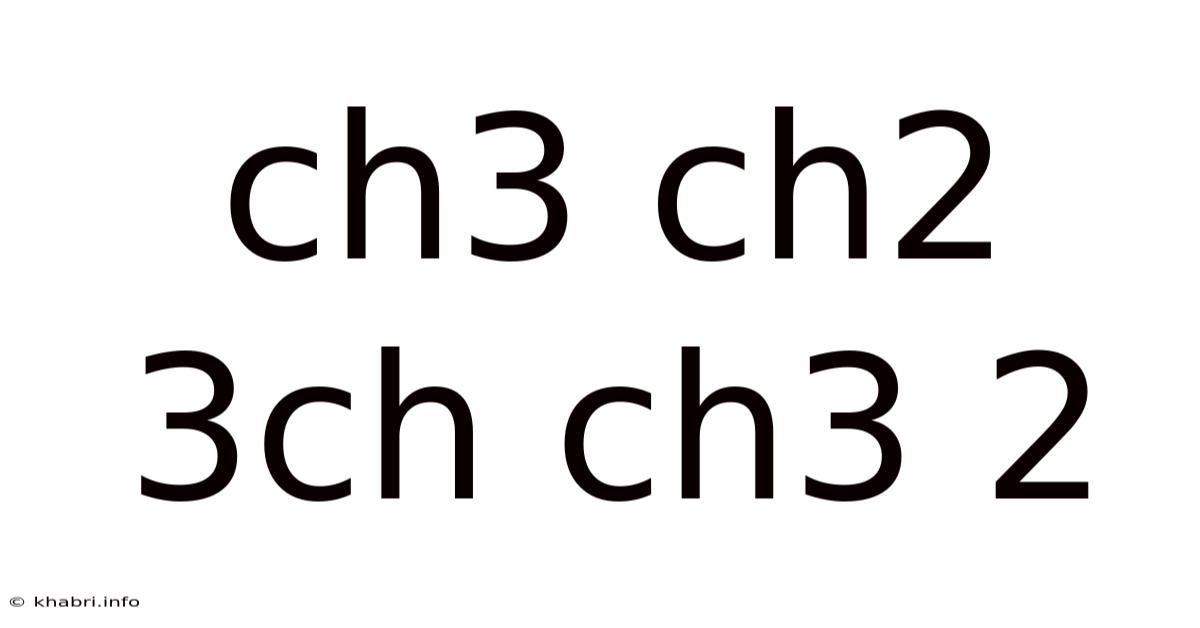
Table of Contents
Decoding the Mystery: Understanding the Structure and Significance of CH3CH2CH(CH3)CH2CH3
This article delves into the chemical structure and properties of the organic compound represented by the formula CH3CH2CH(CH3)CH2CH3. We will explore its IUPAC nomenclature, isomerism, physical properties, chemical reactivity, and potential applications, providing a comprehensive understanding for students and enthusiasts alike. Understanding this seemingly simple formula unlocks a world of chemical intricacies and applications.
Introduction: Unraveling the Formula
The formula CH3CH2CH(CH3)CH2CH3 represents a branched-chain alkane, a type of hydrocarbon. Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons, meaning they contain only single bonds between carbon atoms. The formula indicates the presence of seven carbon atoms (C7) and sixteen hydrogen atoms (H16). Understanding how these atoms are arranged is crucial to understanding the compound's properties. This arrangement dictates the molecule's shape, reactivity, and ultimately, its function. We'll explore this arrangement in detail in the subsequent sections.
IUPAC Nomenclature and Isomerism
The systematic naming of organic compounds is governed by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). To name CH3CH2CH(CH3)CH2CH3 using IUPAC rules, we follow these steps:
-
Identify the longest continuous carbon chain: The longest chain in this molecule contains five carbon atoms. This forms the parent alkane, pentane.
-
Number the carbon atoms: We number the carbon atoms in the longest chain, starting from the end closest to the substituent (the branch).
-
Identify and name the substituents: A methyl group (-CH3) is attached to the third carbon atom.
-
Combine the information: The name becomes 3-methylpentane.
It's crucial to note that isomerism plays a significant role in organic chemistry. Isomers are molecules with the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements. 3-methylpentane is just one isomer of heptane (C7H16). Other isomers exist, such as 2-methylhexane and 2,2-dimethylpentane, each with unique properties. Understanding isomerism is crucial for predicting and interpreting chemical behavior.
Detailed Structural Analysis
Let's break down the 3-methylpentane structure:
-
Carbon Backbone: The main backbone consists of a five-carbon chain (pentane).
-
Methyl Substituent: A methyl group (-CH3), a single carbon atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms, branches off from the third carbon in the main chain.
-
Bonding: All carbon-carbon and carbon-hydrogen bonds are single covalent bonds, indicating a saturated hydrocarbon.
-
3D Structure: The molecule adopts a specific three-dimensional structure, influenced by the tetrahedral geometry around each carbon atom. The bond angles are approximately 109.5 degrees, influencing the molecule's overall shape and interactions with other molecules.
-
Conformations: Alkanes can exist in different conformations due to the rotation around single bonds. These conformations differ in energy and can influence the molecule's properties.
Physical Properties of 3-Methylpentane
Understanding the physical properties of 3-methylpentane is essential for its handling and application. Key properties include:
-
State of Matter: At room temperature and standard pressure, 3-methylpentane exists as a colorless liquid.
-
Boiling Point: The boiling point is relatively low compared to larger alkanes, due to weaker intermolecular forces (van der Waals forces). The precise boiling point depends on factors like purity and pressure.
-
Melting Point: Similar to the boiling point, the melting point is also relatively low.
-
Density: 3-Methylpentane is less dense than water and will float on water.
-
Solubility: Like most alkanes, 3-methylpentane is nonpolar and immiscible (does not mix) with water. It is, however, soluble in many organic solvents.
-
Flammability: 3-methylpentane is highly flammable and should be handled with caution away from ignition sources.
Chemical Reactivity of 3-Methylpentane
Alkanes are generally considered unreactive compared to other classes of organic compounds. However, they can undergo certain reactions under specific conditions:
-
Combustion: The most characteristic reaction of alkanes is combustion, reacting with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide, water, and heat. This is an exothermic reaction, meaning it releases energy.
-
Halogenation: Alkanes can react with halogens (e.g., chlorine, bromine) in the presence of ultraviolet (UV) light. This is a free-radical substitution reaction where a hydrogen atom is replaced by a halogen atom. The reaction can lead to the formation of various halogenated derivatives.
-
Cracking: Under high temperatures and pressures, alkanes can undergo cracking, breaking down into smaller alkanes and alkenes. This process is important in the petroleum industry for producing smaller hydrocarbons that are more suitable for fuels.
Applications of 3-Methylpentane
While 3-methylpentane itself might not have widespread, direct applications compared to some other hydrocarbons, it's often found as a component in:
-
Fuel Mixtures: It can be a component in gasoline or other fuel blends due to its flammability and relatively high energy content.
-
Solvents: Its nonpolar nature makes it a suitable solvent for certain organic compounds in chemical processes or laboratory settings.
-
Chemical Synthesis: It serves as a starting material for the synthesis of other organic compounds.
-
Calibration Standards: Its known physical properties make it useful for calibrating laboratory instruments.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Is 3-methylpentane toxic?
A1: Like many hydrocarbons, 3-methylpentane can be harmful if inhaled or ingested in large quantities. It can act as a central nervous system depressant. Appropriate safety precautions are necessary during handling.
Q2: What are the environmental impacts of 3-methylpentane?
A2: As a hydrocarbon, 3-methylpentane contributes to greenhouse gas emissions when burned. Spills can also contaminate soil and water. Responsible handling and disposal practices are important to minimize environmental impact.
Q3: How is 3-methylpentane produced?
A3: 3-methylpentane is typically obtained as a component of petroleum refining processes. It is separated from other hydrocarbons through fractional distillation.
Q4: Are there any isomers of 3-methylpentane with significantly different properties?
A4: Yes. As mentioned earlier, several isomers exist with different structural arrangements, leading to variations in boiling points, melting points, and other physical properties. The isomeric structure significantly influences the molecule's properties. For instance, 2,2-dimethylpentane exhibits different physical and chemical properties due to the difference in the branched structure.
Conclusion: A Deeper Understanding of a Seemingly Simple Molecule
While the formula CH3CH2CH(CH3)CH2CH3 might appear simple at first glance, a closer examination reveals a wealth of information about its structure, nomenclature, properties, reactivity, and potential applications. This detailed exploration showcases the importance of understanding organic chemistry principles, from basic nomenclature to the intricate world of isomerism and reactivity. This knowledge is fundamental for anyone working in fields related to chemistry, fuel science, and materials science. Further investigation into the reaction pathways, synthesis methods, and detailed analysis of the molecule's behavior under different conditions would enhance a more comprehensive understanding of its application in various industrial and scientific endeavors. The seemingly simple molecule reveals the fascinating complexity of the chemical world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is Fungi Eukaryotic Or Prokaryotic
Sep 12, 2025
-
Nonbonding Electron Pairs On Halogens
Sep 12, 2025
-
Alcohols Contain Which Functional Group
Sep 12, 2025
-
Applied Pathophysiology A Conceptual Approach
Sep 12, 2025
-
Pearson Education Access Code Free
Sep 12, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Ch3 Ch2 3ch Ch3 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.