4 Ethyl 3 4 Dimethyloctane
khabri
Sep 06, 2025 · 6 min read
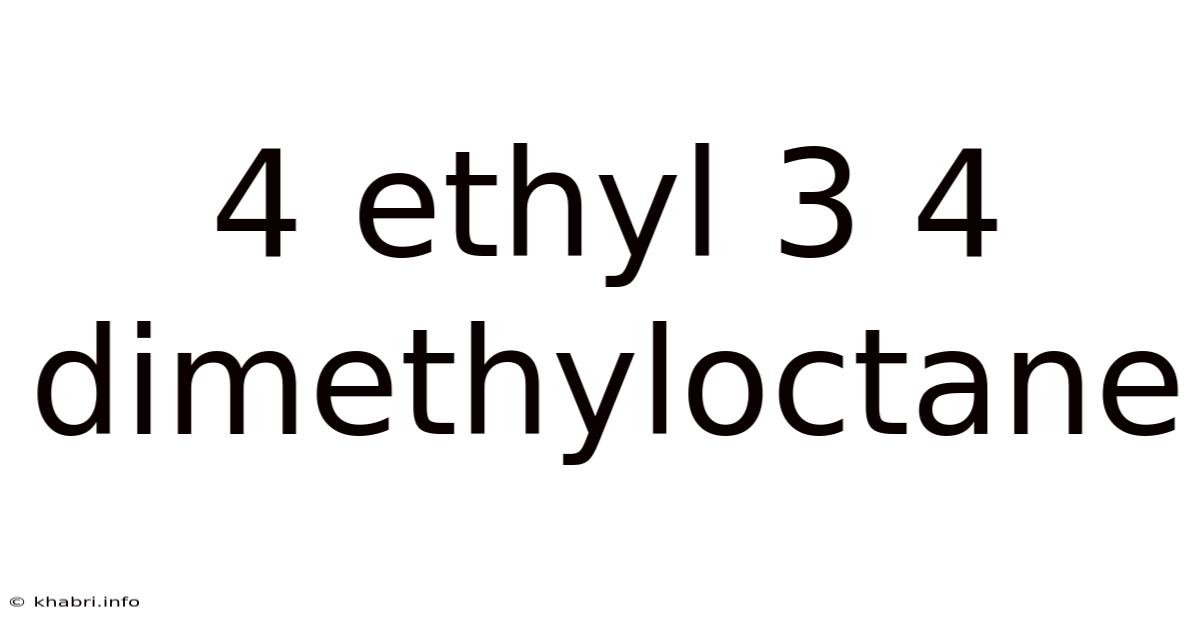
Table of Contents
Decoding 4-Ethyl-3,4-Dimethyloctane: A Deep Dive into its Structure, Properties, and Significance
4-Ethyl-3,4-dimethyloctane is an organic compound, a specific type of alkane, belonging to the vast family of hydrocarbons. Understanding its structure, properties, and potential applications requires a detailed look at its molecular makeup and how it interacts with the world around it. This article will serve as a comprehensive guide, delving into the intricacies of this fascinating molecule. While its specific applications might not be widespread in everyday life, studying it offers a valuable opportunity to understand the principles of organic chemistry and the characteristics of branched alkanes.
Understanding the IUPAC Nomenclature
The name itself, 4-Ethyl-3,4-dimethyloctane, reveals much about the molecule's structure. This systematic naming follows the rules of the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). Let's break it down:
- Octane: This indicates the longest continuous carbon chain contains eight carbon atoms. This is the parent chain upon which other substituents are attached.
- 3,4-Dimethyl: This signifies two methyl groups (–CH₃) are attached to the carbon atoms at positions 3 and 4 along the octane chain. The numbering starts from the end that gives the lowest possible numbers to the substituents.
- 4-Ethyl: An ethyl group (–CH₂CH₃) is attached to the carbon atom at position 4.
Therefore, visualizing the structure is straightforward once we understand the nomenclature. The main chain is eight carbons long, and branches extend from the third and fourth carbon atoms. One branch is a methyl group, and another is an ethyl group, both branching from the same carbon (position 4). This results in a highly branched structure.
Visualizing the Molecular Structure
The best way to grasp the structure is to draw it. You can represent it using several methods:
-
Skeletal Formula: This is a simplified representation showing only carbon-carbon bonds. Carbon atoms are implied at the intersections and ends of lines. Hydrogen atoms are omitted for clarity. In a skeletal formula, the 4-Ethyl-3,4-dimethyloctane will show a main eight-carbon chain with a methyl group branching off carbon 3, and both a methyl and ethyl group attached to carbon 4.
-
Condensed Formula: This shows all atoms, but the bonds are condensed for brevity. A possible condensed formula is CH₃CH(CH₃)C(CH₃)(CH₂CH₃)CH₂CH₂CH₂CH₃. Note that this formula doesn't explicitly define the carbon chain length as clearly as the IUPAC name, highlighting the utility of the systematic naming system.
-
3D Model: A three-dimensional model best represents the molecule’s actual spatial arrangement. This will show the branching and the tetrahedral arrangement of bonds around each carbon atom. Building a 3D model, either physically with molecular model kits or using molecular visualization software, enhances understanding of steric hindrance and molecular shape.
Chemical and Physical Properties
4-Ethyl-3,4-dimethyloctane, like other alkanes, exhibits characteristics typical of non-polar organic compounds:
- State: At room temperature and standard pressure, it's a colorless liquid.
- Solubility: It's practically insoluble in water due to its non-polar nature. However, it’s likely soluble in non-polar organic solvents such as hexane or benzene.
- Boiling Point: The boiling point will be relatively high compared to simpler, unbranched alkanes due to its larger molecular weight and relatively compact structure. Precisely calculating the boiling point without experimental data requires sophisticated computational chemistry techniques. The branched nature will influence the boiling point compared to its straight-chain isomer, n-octane. Branched alkanes typically have lower boiling points than their straight-chain counterparts due to reduced surface area for intermolecular interactions.
- Density: Its density is likely slightly less than water, meaning it will float on water. The exact density will require experimental determination.
- Flammability: Like most alkanes, it's highly flammable and will burn in the presence of oxygen, producing carbon dioxide and water.
- Reactivity: It's relatively unreactive compared to other functional groups due to the strong C-C and C-H single bonds. It does not readily undergo reactions like addition or substitution at room temperature. Reactions might occur under extreme conditions with strong reagents.
Isomerism and Constitutional Isomers
4-Ethyl-3,4-dimethyloctane is just one of many possible isomers of C₁₀H₂₂ (decane). Isomers are molecules with the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements. This specific molecule is a constitutional isomer, meaning its connectivity differs from other C₁₀H₂₂ isomers. The number of possible constitutional isomers for decane is substantial, showcasing the complexity that arises in organic chemistry with even relatively small molecules.
Potential Applications and Significance
While 4-ethyl-3,4-dimethyloctane may not have widespread, specific applications like some other hydrocarbons (e.g., octane in gasoline), its study holds considerable value:
- Research Chemical: It can serve as a model compound in chemical research, specifically studies related to branched alkanes, their properties, and their behavior in various systems. It’s useful for evaluating reaction mechanisms and properties of isomers.
- Understanding Molecular Properties: Studying its properties contributes to a broader understanding of how molecular structure influences physical and chemical characteristics, particularly in the context of branched alkanes and their intermolecular interactions. This allows the prediction of the properties of similar molecules.
- Calibration Standards: It may find application as a calibration standard in analytical techniques such as gas chromatography and mass spectrometry. These techniques require known standards to ensure accurate measurements.
- Component of Petroleum Products: While not a major component, it may be present as a minor constituent in petroleum fractions. The detailed understanding of the composition of petroleum fractions is crucial for optimizing refinery processes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: How is 4-Ethyl-3,4-dimethyloctane produced?
A: It's not typically produced as a single, isolated compound. It would likely be found as a minor component in the distillation of petroleum fractions. Synthetic production would involve complex multi-step organic synthesis methods, not typically cost-effective for such a molecule.
Q: What are the environmental effects of 4-Ethyl-3,4-dimethyloctane?
A: As a hydrocarbon, its release into the environment contributes to greenhouse gas emissions upon combustion. Its biodegradability is relatively low compared to shorter-chain hydrocarbons. However, the specific environmental impact would depend on the quantity released and the specific environment.
Q: Are there any safety concerns associated with 4-Ethyl-3,4-dimethyloctane?
A: As a flammable liquid, it poses a fire hazard. Standard safety precautions associated with handling flammable liquids should be followed. In addition, like many organic solvents, prolonged exposure or inhalation of its vapors should be avoided.
Conclusion
4-Ethyl-3,4-dimethyloctane, although not a household name, offers a significant learning opportunity in organic chemistry. Its intricate structure, detailed naming, and characteristic properties showcase the fundamental principles governing the behavior of organic molecules. While its direct applications might be limited, its role in research and its contribution to a broader understanding of hydrocarbon chemistry are undeniable. This detailed exploration highlights the importance of systematic nomenclature, isomerism, and the relationship between molecular structure and physical properties within the vast landscape of organic compounds. Further research and exploration of its properties, using advanced techniques like computational chemistry and spectroscopic analysis, will help refine our understanding of its behavior and potential uses.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Molar Mass Of Anhydrous Salt
Sep 06, 2025
-
Exercise 13 Problems Part 2
Sep 06, 2025
-
Substrate Level Phosphorylation Occurs In
Sep 06, 2025
-
Identify The Predominant Intermolecular Force
Sep 06, 2025
-
In The Accompanying Graph Place
Sep 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 4 Ethyl 3 4 Dimethyloctane . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.