3 Isopropyl 2 4 Dimethylpentane
khabri
Sep 12, 2025 · 6 min read
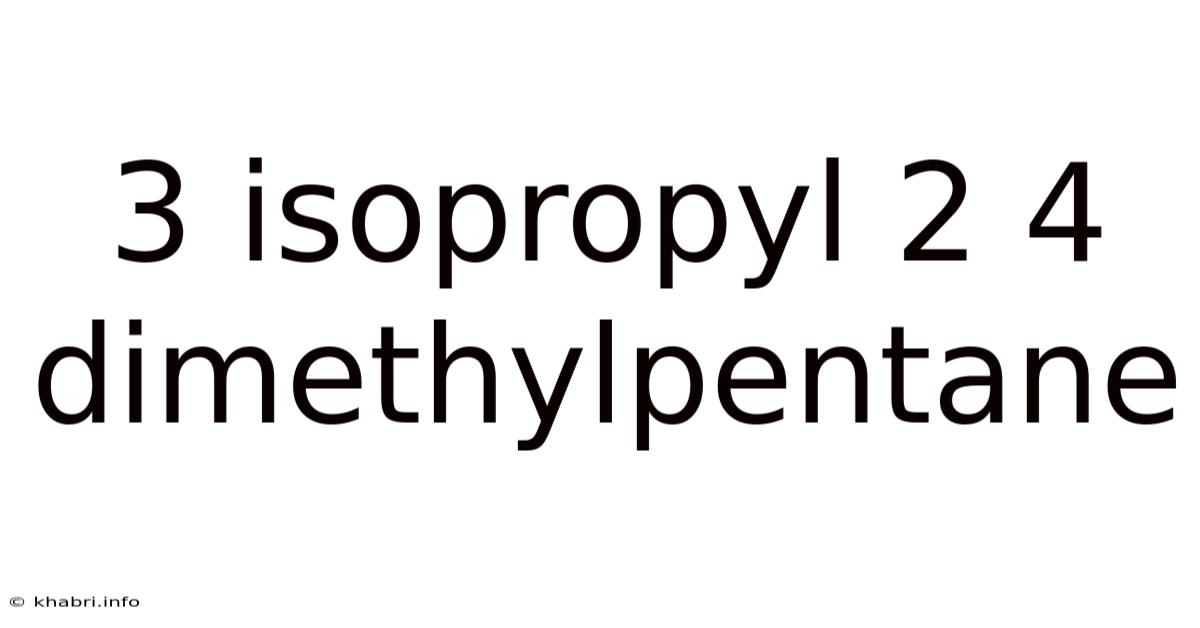
Table of Contents
Decoding 3-Isopropyl-2,4-dimethylpentane: A Deep Dive into its Structure, Properties, and Significance
3-Isopropyl-2,4-dimethylpentane is an organic compound, specifically an alkane, belonging to the broader family of branched-chain hydrocarbons. Understanding its structure, properties, and potential applications requires a detailed look at its chemical makeup and behavior. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of this molecule, exploring its nomenclature, isomerism, physical properties, potential chemical reactions, and its significance within the larger context of organic chemistry.
Understanding the Nomenclature: Breaking Down the Name
The name "3-isopropyl-2,4-dimethylpentane" itself provides a roadmap to its structure. Let's dissect it:
-
Pentane: This indicates a five-carbon chain as the parent alkane. Imagine a straight chain of five carbon atoms.
-
Dimethyl: This signifies the presence of two methyl groups (-CH₃). The numbers "2" and "4" specify their positions on the pentane chain. So, one methyl group is attached to the second carbon atom, and another to the fourth.
-
Isopropyl: This refers to an isopropyl group, (-CH(CH₃)₂), which is a branched alkyl group consisting of a central carbon atom bonded to two methyl groups and one other carbon atom. The "3" indicates that this isopropyl group is attached to the third carbon atom of the pentane chain.
Putting it all together, we can visualize 3-isopropyl-2,4-dimethylpentane as a branched-chain alkane with a five-carbon backbone, two methyl groups, and an isopropyl group strategically placed along the chain.
Structural Isomerism: Exploring the Possibilities
Isomerism is a crucial concept in organic chemistry. Isomers are molecules that share the same molecular formula but differ in their arrangement of atoms. 3-isopropyl-2,4-dimethylpentane has several structural isomers, meaning molecules with the same molecular formula (C₁₁H₂₄) but with different branching patterns. These isomers will exhibit varying physical and chemical properties despite their identical chemical composition. Identifying and distinguishing these isomers is a fundamental task in organic chemistry. Determining the exact structure of an unknown compound often requires advanced techniques like Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy and Mass Spectrometry (MS).
Physical Properties: A Detailed Examination
The physical properties of 3-isopropyl-2,4-dimethylpentane are largely dictated by its nonpolar nature and relatively high molecular weight. Key characteristics include:
-
State: At room temperature and standard pressure, it exists as a colorless liquid.
-
Boiling Point: Due to its branched structure and relatively strong van der Waals forces, it will have a relatively high boiling point compared to linear alkanes of similar molecular weight. The exact boiling point requires experimental determination. Branching reduces the surface area available for intermolecular interactions, leading to lower boiling points compared to their linear counterparts.
-
Melting Point: Similar to the boiling point, the melting point will also be influenced by the molecule's structure and intermolecular forces. Again, experimental data is necessary for precise determination.
-
Density: The density will be lower than that of water, as is typical for most hydrocarbons.
-
Solubility: Being a nonpolar molecule, it is essentially insoluble in water but readily soluble in other nonpolar organic solvents.
Chemical Reactions: Reactivity and Potential Applications
As an alkane, 3-isopropyl-2,4-dimethylpentane is relatively unreactive under normal conditions. However, under specific conditions and with appropriate catalysts, it can undergo several important reactions:
-
Combustion: Like all alkanes, it readily undergoes combustion in the presence of oxygen, producing carbon dioxide, water, and heat. This reaction is the basis for its potential use as a fuel.
-
Halogenation: In the presence of UV light or heat, it can react with halogens (like chlorine or bromine) via a free radical mechanism. This substitution reaction replaces one or more hydrogen atoms with halogen atoms. The reaction is not highly selective; multiple products may form due to the various positions where substitution can occur.
-
Isomerization: Under specific catalytic conditions, it can undergo isomerization, rearranging its structure to form different isomers. This process can be used to produce more desirable isomers with specific properties.
-
Cracking: At high temperatures and pressures, in the presence of catalysts, it can undergo cracking – a process that breaks down larger molecules into smaller, more useful hydrocarbons. This is a common process in the petroleum refining industry.
Significance and Applications: Exploring its Role
While 3-isopropyl-2,4-dimethylpentane may not have widespread individual applications in the same way as some other organic compounds, its significance lies within its role in the broader context of:
-
Petroleum Refining: It's a component found in petroleum, and understanding its properties and behavior is crucial for efficient refining processes. The refining process involves separating and purifying different hydrocarbons present in crude oil, and knowledge of individual compounds like 3-isopropyl-2,4-dimethylpentane helps optimize these procedures.
-
Fuel Production: Its combustion properties make it a potential component of gasoline blends, though its precise contribution would depend on factors like octane rating and other blend components. Octane rating is a measure of a fuel's resistance to knocking or pinging in an engine.
-
Chemical Synthesis: While not a direct starting material for many common products, it can serve as an intermediate in the synthesis of more complex molecules. Its reactivity, although limited, can be exploited under specific conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the IUPAC name for 3-isopropyl-2,4-dimethylpentane?
A: 3-Isopropyl-2,4-dimethylpentane is already the correct and unambiguous IUPAC name.
Q: Is 3-isopropyl-2,4-dimethylpentane toxic?
A: Like many hydrocarbons, it is considered relatively non-toxic at low concentrations. However, high concentrations can cause respiratory irritation and other health problems. Appropriate safety precautions should always be observed when handling any organic solvent.
Q: What are the environmental impacts of 3-isopropyl-2,4-dimethylpentane?
A: As a hydrocarbon, its combustion contributes to greenhouse gas emissions. Spills can contaminate soil and water, though its impact is usually considered less severe than those of some other pollutants.
Q: Can 3-isopropyl-2,4-dimethylpentane be synthesized in a laboratory?
A: While feasible, synthesizing this specific compound is not a common laboratory procedure. It is more practical to isolate it from petroleum fractions.
Conclusion: A Comprehensive Overview
3-isopropyl-2,4-dimethylpentane, although not a household name, exemplifies the complexity and diversity within the world of organic chemistry. Understanding its structure, properties, and potential reactions provides valuable insight into the broader field of hydrocarbon chemistry and its relevance to industries like petroleum refining and fuel production. This detailed exploration showcases the importance of systematic nomenclature, isomerism, and the correlation between molecular structure and macroscopic properties. Further research, particularly involving spectroscopic and analytical techniques, would be crucial for a more thorough characterization of its behavior and potential applications. The information provided here serves as a foundation for deeper investigation and a more comprehensive understanding of this specific branched alkane within the wider spectrum of organic molecules.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Multi Step Income Statement Wileyplus
Sep 12, 2025
-
Economic Profits Are Equal To
Sep 12, 2025
-
Raw Materials Inventory T Account
Sep 12, 2025
-
Average Annual Net Cash Inflow
Sep 12, 2025
-
Table 20 3 Blood Typing Results
Sep 12, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 3 Isopropyl 2 4 Dimethylpentane . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.